Sample Collection Techniques
Adequate restraint of the turtle is required for any procedure. Chemical restraint should be utilized when appropriate, however, manual restraint is typically all that is required for blood draws. Removing a turtle from the water may be challenging if they are active and feisty, and having well trained personnel handling the turtle will reduce the stress level for the animal and the veterinarian.
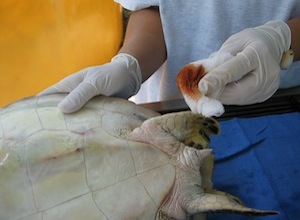
Normal dermal flora of sea turtles can cause infection if inadvertently carried inward by a needle stick. Although sterile preparation of the sampling site with a 5-minute scrub is not needed, the site should be generally cleaned with a topical antimicrobial such as betadine or chlorhexiderm.
Vaccutainers or syringes may be used for blood collection, but all samples should be heparinized. Slides made immediately after collection allow for cytology and estimate of cell counts.
Venipuncture sites
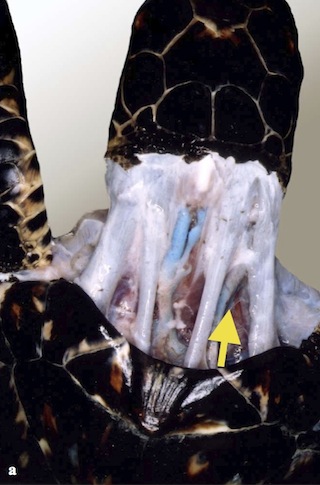
Dorsal Cervical Vessels
- Located in lateral dorsal cervical region (left and right)
- Can also be located centrally
- From margin of nuchal scute (1st vertebral) draw an imaginary line to the tympanic scale on the side of the skull. The vein will be between the tendons in the first to middle third of the neck
- Needle is held approximately 90 degrees to the skin
- Mid cervical
- Neck must be extended
- Reliable for blood collection
- Difficult to maintain for injection
Photo credit: Jeanette Wyneken
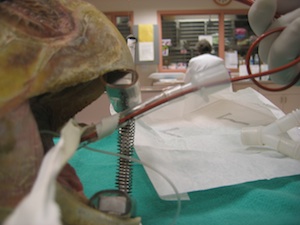
Subcarapacial Sinus
- Accessed from the midline of the body
- Needle is held parallel to the long axis
- Located approximately 1 cm ventral to the carapace
- Does not require extension of the neck so it is good for uncooperative patients
- Good location for short term (several hours) intravenous catheter placement
- Large volumes of fluid may given rapidly through this sinus
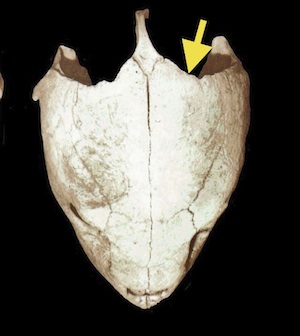
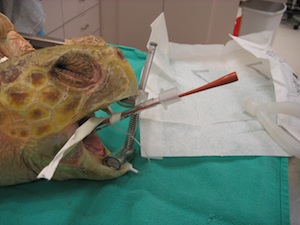
Post Occipital Sinus
- In parietal notch, halfway up the supraoccipital crest
- Needle is held at 45 degree angle to midline
- Hit bone of skull
- Reliable for injection or blood draw
- Excellent with uncooperative patients as neck may be ventroflexed or in normal position
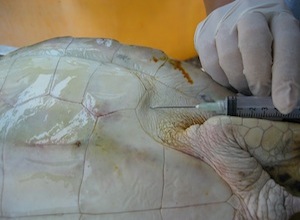
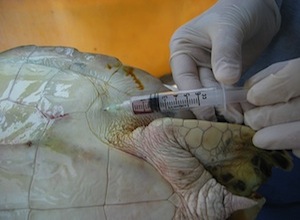
This method may be used to tap the coelomic cavity for fluid or gas if noted. There is no diaphragm in sea turtles to separate the thorax from the abdomen, so the large common cavity is referred to as the coelom. If the turtle is tilted sideways, the down side can be used to sample fluid and the up side can be used to drain gas. Injectable medications can also be put directly into the coelom. This route is extremely effective for fluid administration. After cleaning the inguinal fossa with an antimicrobial solution, a long needle may be introduced through the skin and soft tissue into the coelom by directing the needle toward the shoulder on the same side. This may also be done with the patient in sternal recumbency if the individual is too large to tip onto one side. If negative pressure is encountered on aspiration, advance the needle a bit further in order to make sure you are into the body cavity. When the needle is through the coelomic lining there is no resistance and the fluid rate can be quite fast if the gauge of the needle is large enough. If upon aspiration, urine or fecal matter is encountered, abort the procedure and try again with new needle and syringe. (Note: the final photo illustrates needle placement on a cadaver.)
Note - For bacteria and/or fungal cultures it is important to inform the lab that the specimen was obtained from a sea turtle.